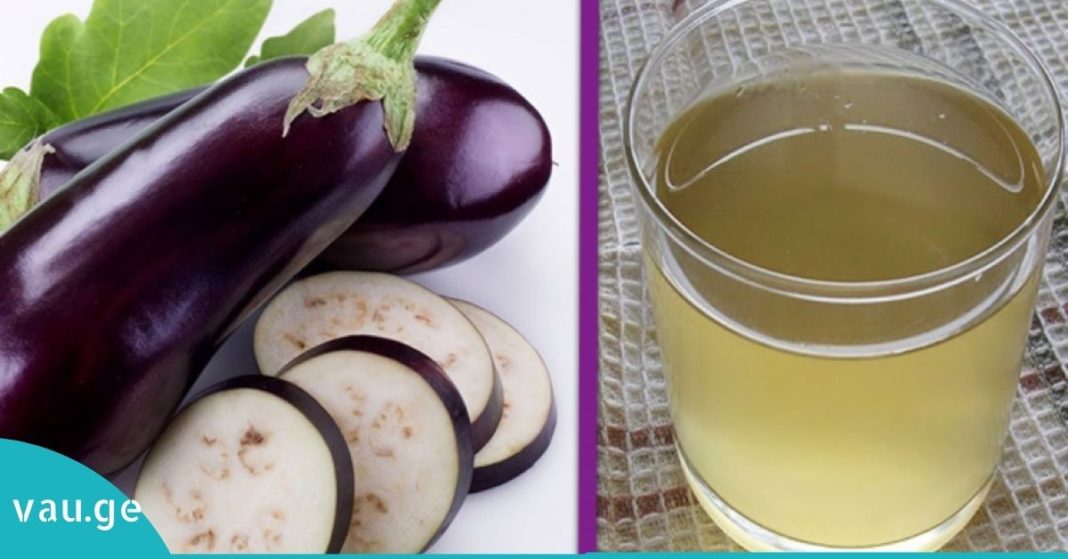
Eggplants, often overlooked in everyday diets, are actually a nutritional powerhouse loaded with vitamins, minerals, and potent phytochemicals. Consuming them regularly may offer a wide array of health benefits — in fact, some researchers suggest that eggplants can be more effective than certain medications for promoting overall well-being. Here are ten compelling reasons to make eggplants a regular part of your meals:
- Improves Brain Function
One of the most notable compounds in eggplant is nasunin, a powerful antioxidant found in the purple skin of the vegetable. Nasunin is a type of anthocyanin, a phytochemical that protects brain cell membranes from damage caused by free radicals. By neutralizing these unstable molecules, eggplant helps preserve cognitive function, potentially reducing the risk of age-related brain disorders like Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. - Supports Heart Health
A controlled study on animals showed that consuming a specific amount of eggplant juice significantly reduced cholesterol levels in artery walls. This implies that regular eggplant consumption may help prevent atherosclerosis and related cardiovascular issues. The antioxidants and phytonutrients in eggplant also promote blood vessel flexibility, reduce inflammation, and improve circulation. - Aids in Weight Loss
Trying to shed some pounds? Eggplant might be your new best friend. With only 35 calories per cup, it’s a filling but low-calorie food. More importantly, it contains a compound called saponin, which helps block the absorption of fat in the digestive system. Drinking a glass of eggplant juice after meals has been recommended by some experts as a natural way to reduce fat absorption and promote better kidney function due to its diuretic properties. - Lowers Blood Pressure
Eggplant is rich in anthocyanins, particularly delphinidin, which has been linked to improved blood pressure regulation. A recent clinical study revealed that participants who regularly consumed anthocyanin-rich foods like eggplant experienced noticeable drops in their blood pressure. This makes it an excellent addition for those seeking natural ways to manage hypertension.
- Improves Brain Function
- Combats Free Radicals
One of eggplant’s most potent antioxidants is chlorogenic acid, known for its powerful ability to neutralize harmful free radicals. This compound not only protects cells from oxidative damage but also has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, contributing to overall cellular health and longevity. - Low-Calorie, Nutrient-Dense
One serving of eggplant — about one cup cooked — contains just 35 calories, yet it is rich in fiber, vitamins (such as B1, B6, and K), and minerals (like copper, manganese, and potassium). This makes it a smart choice for anyone looking to eat more nutritiously without consuming excess calories. - Reduces Stress and Oxidative Damage
Eggplants contain a variety of bioflavonoids, which are plant-based compounds with antioxidant effects. These substances help stabilize blood pressure and reduce the impact of oxidative stress. Chronic oxidative stress has been linked to the development of various diseases, including cancer, and eggplants offer a natural way to counteract it. - Helps Regulate Blood Sugar
Dietary fiber plays a critical role in managing blood sugar levels, and eggplants are an excellent source. Research shows that regular intake of fiber can reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes by up to 20%. The fiber in eggplant slows the rate of digestion and the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, helping to prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Combats Free Radicals
- Delicious and Versatile in the Kitchen
Beyond its health benefits, eggplant is also incredibly versatile and delicious. It can be roasted, grilled, baked, or pureed into spreads. One popular dish includes roasted eggplant with red bell peppers, seasoned with garlic and olive oil. During eggplant season, salads and dips made with eggplant become popular staples in many households. - May Help Fight Cancer
Emerging research has suggested that certain compounds in eggplant, including solasodine rhamnosyl glycosides (SRGs), may help destroy cancer cells. These naturally occurring phytonutrients have shown promise in preclinical studies for reducing tumor size and preventing the spread of certain cancer cells when consumed in regular, moderate amounts.
Conclusion:
Eggplant is far more than just a colorful addition to your dinner plate. With its unique combination of nutrients, antioxidants, and disease-fighting compounds, it offers an impressive array of health benefits — from supporting the brain and heart to helping manage blood sugar and fight cancer. Incorporating more eggplant into your diet could be a simple, natural way to protect your health — perhaps even more effectively than some commonly used medications. So next time you’re planning a meal, don’t forget the eggplant!