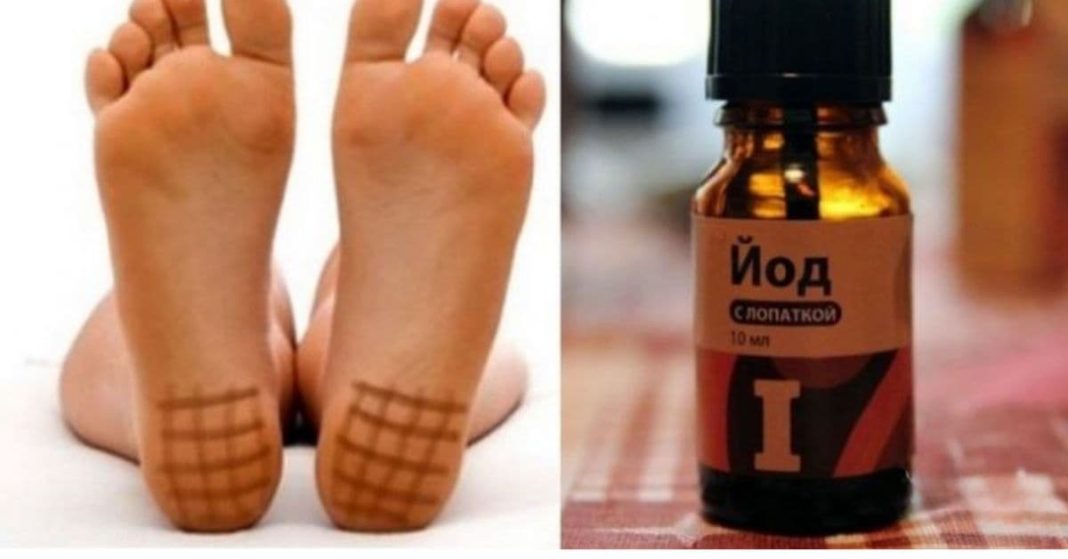
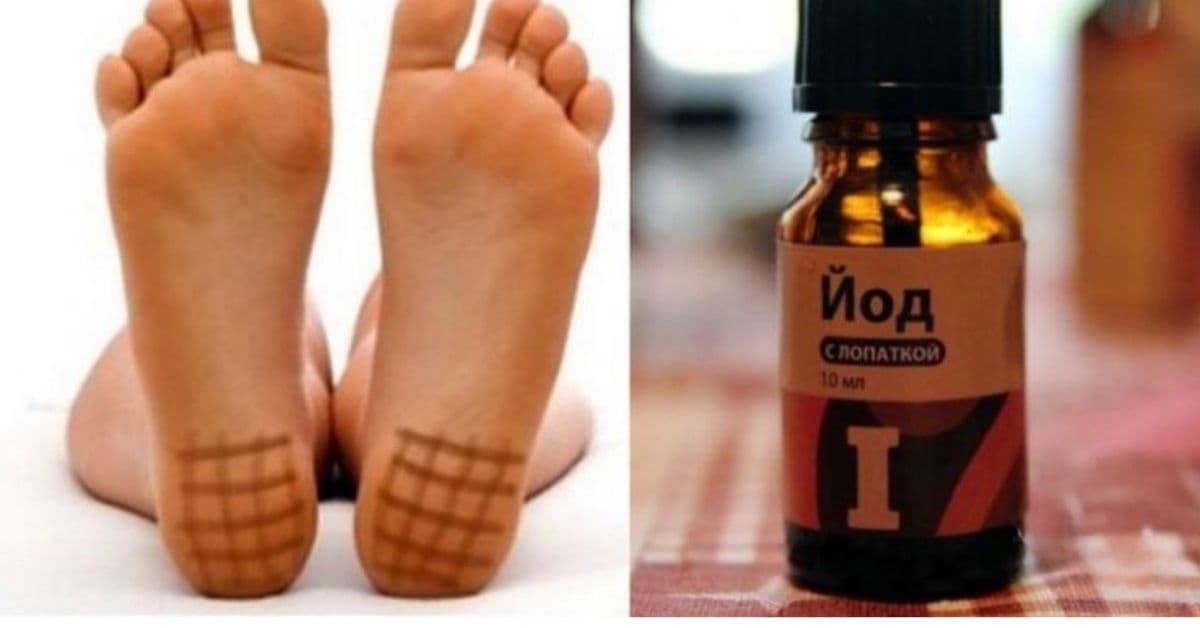
Many traditional home remedies have been passed down through generations, and one of the most intriguing among them is the iodine grid, often applied to different parts of the body. While it may seem like an old-fashioned technique, the iodine grid drawn on the heels is still widely used because of its surprising benefits. People who spend long hours standing or walking often turn to this method to relieve discomfort, ease swelling, and stimulate circulation. Even though it looks simple, the practice carries several fascinating aspects worth understanding.

This expanded guide explores how the iodine grid works, what it can tell you about your body, and how to safely use it at home. As with any remedy, understanding the process and proper precautions is essential to ensuring safety and effectiveness.
Why the Iodine Grid Is Applied to the Heels
The heel area contains thick skin and numerous small blood vessels. When iodine is applied in a grid pattern, the skin absorbs it gradually, allowing the iodine to influence circulation in that localized region. Many people who are on their feet for most of the day—nurses, teachers, retail workers, and individuals with physically demanding jobs—experience swelling, heaviness, or fatigue in the legs. The iodine grid technique is believed to relieve this discomfort by warming the skin and increasing blood flow.
Another notable effect of iodine is its ability to slightly lower body temperature. This has made it a popular nighttime remedy, especially for those who want to relax their legs before sleep or reduce mild inflammation. For that reason, the iodine grid is commonly applied at night, followed by putting on warm socks to boost the warming effect.
A Traditional Method With an Unexpected Diagnostic Benefit
One of the most interesting aspects of the iodine grid technique is that it is sometimes used as an informal indicator of iodine levels in the body. Many people believe that the rate at which the grid disappears can hint at whether the body is iodine-deficient.
If the grid fades entirely overnight, it is often taken as a sign that the body quickly absorbed the iodine, which might suggest a need for more iodine-rich foods such as seafood, seaweed, or iodized salt. Conversely, if the grid remains visible for many hours or even the entire following day, some interpret this as an indication that the body’s iodine levels are sufficient.
Although this is not a scientifically precise diagnostic method, it is a popular folk indicator that people continue to use out of curiosity or tradition. It offers a way to observe how your skin and body react, even if it should not replace medical testing or professional advice.
Important Precaution: Check for Iodine Allergy First
Before drawing an iodine grid on your heels, it is crucial to ensure that you are not allergic to iodine. Although iodine allergies are relatively uncommon, they can cause skin irritation, redness, burning sensations, or swelling if present. Performing a patch test is a simple and safe way to avoid complications.
To test for sensitivity, draw a small line or tiny square of iodine on the inside of your wrist. Leave it for about 15–30 minutes without washing it off. If you do not experience redness, itching, discomfort, or any changes in the skin, you can proceed confidently. However, if irritation occurs, it is best to avoid using iodine on larger areas of the body.
This preliminary step is essential because the skin on the heels, although thicker, can still react negatively if you have an allergy or sensitivity.
How to Properly Draw the Iodine Grid
Once you confirm that you are not allergic, you can move on to applying the iodine grid itself. The process is simple, but following the correct technique ensures the best results.
You should never apply iodine in a thick, heavy layer. Instead, use a thin application that allows the substance to absorb evenly. A cotton swab, such as a Q-tip, works perfectly because it helps you draw neat, precise lines.
The grid is made by drawing evenly spaced horizontal and vertical lines so that they create small squares. The ideal size for each square is approximately one by one centimeter. This pattern allows the iodine to penetrate the skin gradually and uniformly.
After drawing the grid, allow it to dry for a minute or two before putting on socks or moving around. The most common recommendation is to perform this technique before going to bed because nighttime rest helps the iodine absorb more effectively. Wearing warm socks afterward enhances circulation and increases the comfort of tired, swollen feet.
Why You Should Not Overuse This Remedy
Despite its benefits, the iodine grid should not be used excessively. Because iodine is absorbed through the skin, frequent use can potentially lead to excessive iodine accumulation, which may affect thyroid function. Modern practitioners of home remedies usually recommend applying the grid no more than three to four times a week.
This moderate approach ensures that you can enjoy the improvements in circulation and comfort without putting unnecessary strain on your body. Like many natural remedies, balance and moderation are key.
A Simple Yet Effective Technique for Leg Relief
When used properly, the iodine grid technique can provide welcome relief from swelling, tension, and fatigue in the feet and legs. It is easy, inexpensive, and requires no special preparations besides a bottle of iodine and a cotton swab. For people who spend many hours standing, the method can become a comforting nighttime ritual that eases the transition into restful sleep.
Beyond its physical benefits, the iodine grid has a traditional, almost nostalgic appeal. Many people remember this method being used by parents or grandparents, and reviving it can feel like reconnecting with time-tested wisdom that relied on simple but effective household ingredients.
Conclusion
Drawing an iodine grid on your heels is a surprisingly beneficial practice that blends tradition with practicality. It improves circulation, helps reduce swelling, and serves as an informal indicator of iodine levels in the body. The method is easy to perform, requires minimal supplies, and can bring significant comfort when used appropriately.
Always remember to check for allergies first and avoid overusing iodine. When integrated sensibly into your routine, this folk remedy can become a relaxing and rejuvenating part of your self-care practices—one that many people still find surprisingly effective even today.
Vau.ge – Your Daily Guide for Practical Advice!
Vau.ge is a place where caring for your health, beauty, and daily routines becomes a natural, accessible, and enjoyable experience. Our main goal is to provide you with reliable information about natural remedies, homemade recipes, and practical tips that help you live a healthier life, look better, and simplify your everyday tasks without unnecessary expenses.
Our tips are easy to incorporate into your everyday life — whether it’s skincare, haircare, health-boosting remedies, or small tricks to save time. This knowledge will not only improve your own life but also allow you to share the experience with others, giving more people the chance to live a balanced life naturally and economically.
Please note: The articles on our website are for informational purposes only and do not replace professional medical advice. If you have serious health concerns, please consult a qualified specialist.