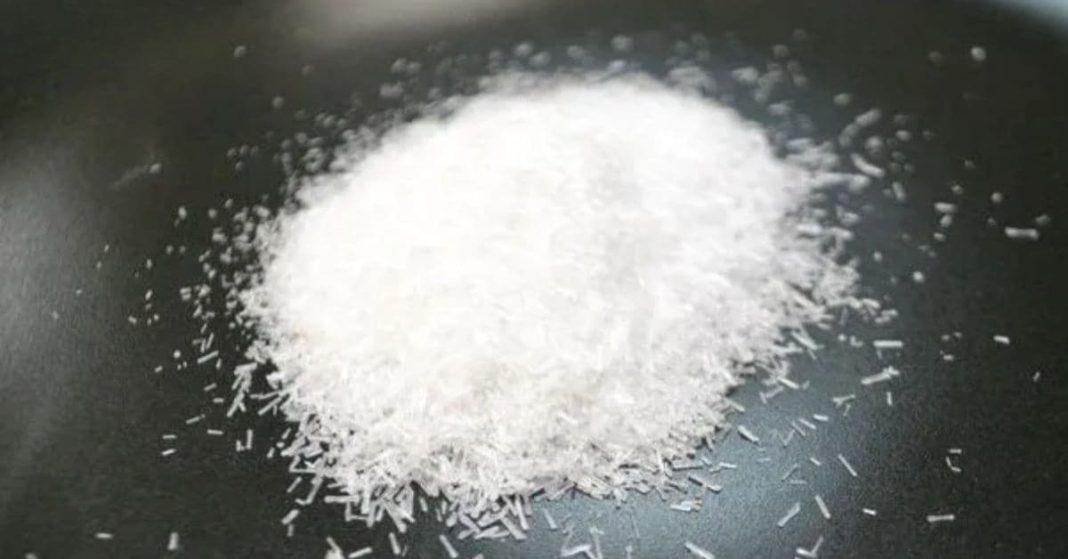
In today’s fast-paced world, we often pay little attention to the ingredients in the foods we consume daily. While many additives seem harmless at first glance, some have profound long-term effects on our health. One such silent threat is monosodium glutamate (MSG), also labeled as E621, a common flavor enhancer that can dramatically alter not only the taste of food but also the way our bodies and brains react to it.
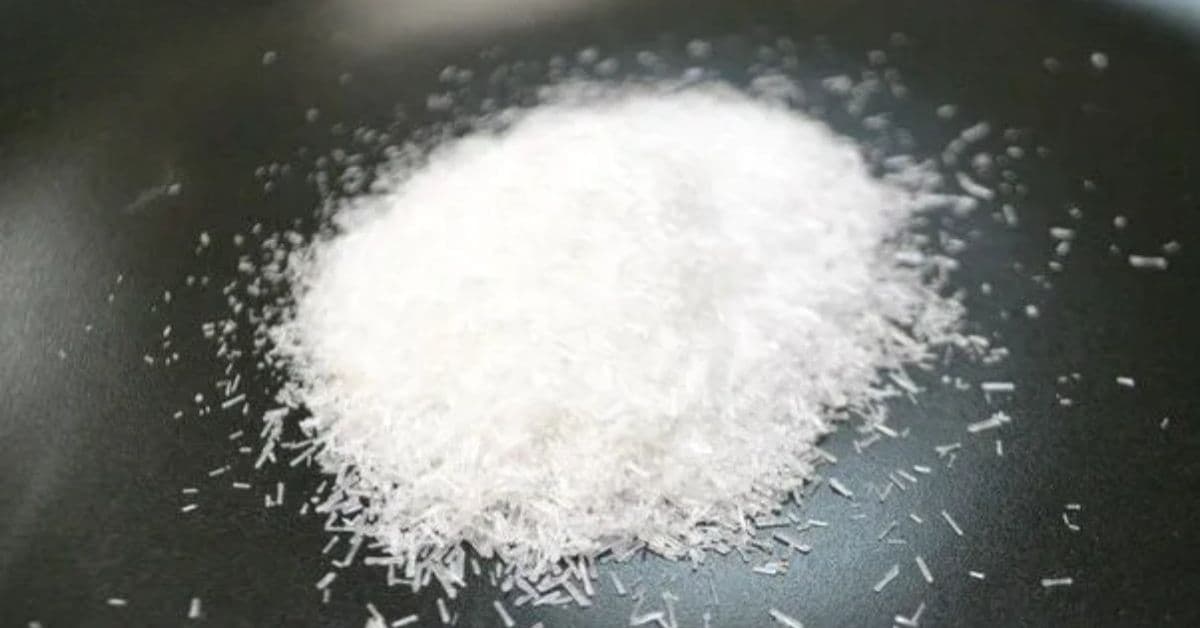

This article explores why MSG is considered one of the most dangerous additives in modern diets, how it affects the body, and practical steps you can take to avoid it.
What Is Monosodium Glutamate (E621)?
Monosodium glutamate, or MSG, was first discovered in 1907 by Japanese chemist Kikunae Ikeda, who noticed that it could enhance the savory taste of foods. Today, MSG is widely used in restaurants, fast food, frozen meals, and processed snacks to improve flavor and increase consumer appeal. It is often added as a substitute for salt and is found in sauces, chips, hot dogs, canned soups, and even some beverages.
At first glance, MSG may seem harmless, especially since small amounts are generally considered safe for adults. The recommended daily limit is 1.5 grams for adults and less than 0.5 grams for children. However, its widespread use and its effects on appetite and metabolism make it a significant concern.
How MSG Affects the Body
MSG acts on the brain in ways similar to certain drugs. It stimulates brain cells, enters the bloodstream, and can even influence the genes responsible for taste perception. This stimulation increases cravings and encourages overeating, which contributes to obesity.
Frequent consumption of MSG-rich foods can disrupt the natural balance of appetite signals in the brain, leading to a cycle of dependency. Many people find themselves unconsciously reaching for snacks or processed foods containing MSG, often without realizing why they cannot resist.
The Dangers of MSG
Excessive intake of MSG is linked to a variety of symptoms collectively known as the “Chinese Restaurant Syndrome.” These can include:
- Nausea
- Chest pain
- Headaches or migraines
- Drowsiness and fatigue
- Dizziness
- Visual disturbances
- Hormonal imbalances
- General weakness
Beyond these immediate symptoms, long-term consumption can contribute to more serious health issues, including obesity, metabolic disorders, and cardiovascular strain. This is especially concerning for children, who are more sensitive to MSG and may experience its effects at even lower doses.
Why Food Manufacturers Use MSG
The prevalence of MSG in processed foods is not accidental. Large food producers use this additive to:
- Enhance flavor without increasing production costs
- Make lower-quality ingredients taste better
- Increase sales by creating addictive taste profiles
This widespread use makes it difficult for consumers to avoid MSG, especially when it appears in seemingly healthy foods like canned vegetables or frozen meals. MSG is particularly insidious because it not only enhances flavor but also encourages repetitive consumption, creating a subtle form of dependency.
How to Protect Yourself
Fortunately, there are practical steps you can take to minimize MSG intake and protect your health:
- Read labels carefully: MSG can appear under many names, including monosodium glutamate, hydrolyzed vegetable protein, autolyzed yeast extract, and yeast extract. Avoid products that list E621.
- Limit processed foods: Chips, sauces, fast food, and pre-packaged meals are the most common sources of MSG.
- Use natural seasonings: Herbs, spices, lemon juice, garlic, and other natural flavor enhancers can provide taste without the harmful effects of MSG.
- Cook at home whenever possible: Preparing meals from scratch allows you to control ingredients and avoid hidden additives.
Recognizing Hidden MSG
MSG is often hidden in foods that appear healthy. For example, some salad dressings, soups, and even beverages contain this additive. This makes vigilance essential. Becoming aware of MSG’s presence in your diet is the first step toward protecting your health and preventing long-term complications.
The Bottom Line
Monosodium glutamate is not just a flavor enhancer—it is a chemical that can influence your appetite, metabolism, and overall health. Over time, frequent consumption can lead to overeating, weight gain, hormonal imbalances, and other serious health consequences. By understanding the risks and learning to identify MSG in everyday foods, you can take meaningful steps to safeguard your health.
Avoiding MSG may seem challenging at first, but with careful attention to labels, cooking at home, and choosing natural ingredients, you can significantly reduce your exposure. Your body will thank you in the long run, as avoiding this “silent killer” can improve digestion, energy levels, and overall well-being.
Remember: the simplest step toward better health is awareness. Once you know what to avoid, you can make informed choices and reclaim control over your diet.
Vau.ge – Your Daily Guide for Practical Advice!
Vau.ge is a place where caring for your health, beauty, and daily routines becomes a natural, accessible, and enjoyable experience. Our main goal is to provide you with reliable information about natural remedies, homemade recipes, and practical tips that help you live a healthier life, look better, and simplify your everyday tasks without unnecessary expenses.
Our tips are easy to incorporate into your everyday life — whether it’s skincare, haircare, health-boosting remedies, or small tricks to save time. This knowledge will not only improve your own life but also allow you to share the experience with others, giving more people the chance to live a balanced life naturally and economically.
Please note: The articles on our website are for informational purposes only and do not replace professional medical advice. If you have serious health concerns, please consult a qualified specialist.