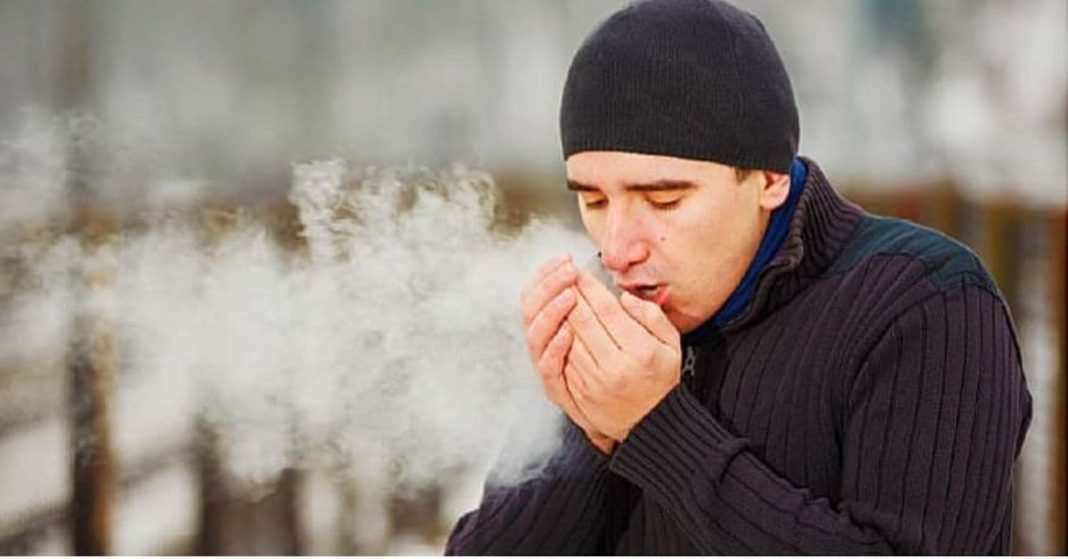
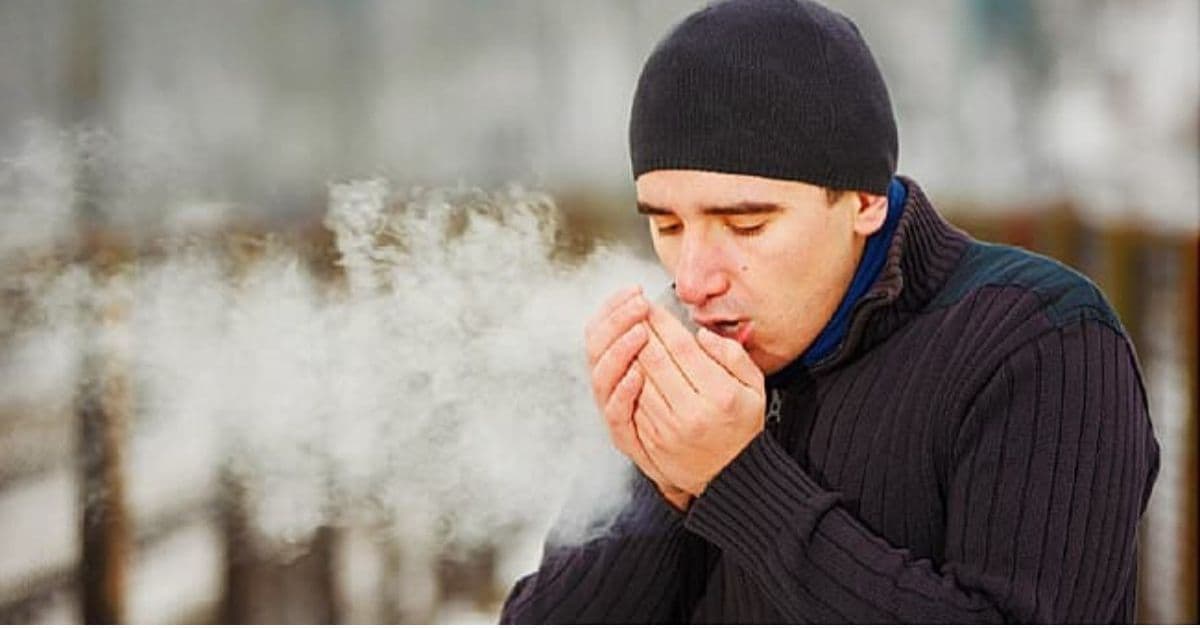
Cold weather is a challenge for many people, but for some, it triggers more than simple discomfort. There is a real condition known as cold allergy, also referred to as cold-induced urticaria, in which the body reacts painfully and aggressively to exposure to low temperatures. For individuals who experience this sensitivity, winter winds, cold water, icy air, or even something as simple as eating ice cream can provoke uncomfortable and sometimes alarming symptoms. Although often underestimated, cold allergy can significantly disrupt daily life and reduce overall comfort. Understanding why it happens and how to protect yourself is essential for managing the condition effectively.

What Is Cold Allergy?
Cold allergy is the body’s abnormal immune response to cold temperatures or cold contact. This reaction can be triggered by a variety of cold stimuli such as snow, strong winter wind, a sudden temperature drop, or contact with cold food and drinks. When the skin or mucous membranes encounter these cold factors, the immune system responds as if exposed to an allergen. This leads to a cascade of symptoms that resemble a traditional allergic reaction.
While many people assume that cold allergy is simply dry or irritated skin, the mechanism behind it is more complex. The reaction often appears in the form of skin irritation — welts, redness, itching, or even swelling. In more intense cases, it can cause deeper swelling of the lips, fingers, or even the tongue after consuming cold beverages or ice cream. These symptoms are uncomfortable but also serve as important signals from the body that something is not functioning as it should.
Why Does Cold Allergy Occur?
The root of cold allergy lies in the heightened sensitivity of dermal cells to temperature changes. When these cells are overly responsive, the body reacts to cold exposure as though it is encountering a harmful allergen. The immune system then releases histamines into the bloodstream. Histamines are chemical substances responsible for managing inflammatory and allergic responses.
Once released, histamines increase the permeability of capillary walls. This allows fluids to escape into surrounding tissues, especially in areas that were in direct contact with the cold. As a result, visible symptoms occur — swelling, redness, itchiness, bumps, or hives. These reactions can vary in intensity from person to person: some individuals may experience only mild irritation, while others may suffer from strong, painful swelling and persistent discomfort.
Genetic predisposition plays an important role as well. People who have a family history of allergies are naturally more likely to develop cold-induced reactions. Additionally, chronic health conditions may weaken the body, creating an environment where cold allergy is more likely to appear.
Who Is at Higher Risk?
Although cold allergy can affect anyone, certain groups are at greater risk. These include:
- Children and teenagers, whose immune systems are more reactive.
- Individuals with chronic conditions, such as hepatitis or autoimmune diseases.
- People with family histories of allergies, making them more vulnerable to allergic reactions in general.
While the condition is not contagious, it can be persistent. Some individuals experience symptoms only in early adulthood, while others face them throughout their lives. Understanding your personal risk factors can help you prevent or minimize uncomfortable reactions.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Cold Allergy
Symptoms typically appear shortly after cold exposure and may range from mild to severe. One of the most common signs is hives — red, itchy patches or welts that form on the skin. These may appear when stepping into cold weather, swimming in cold water, or entering a heavily air-conditioned room. When the person warms up, itching and redness often intensify before gradually fading away.
In more pronounced cases, individuals may notice that their fingers swell or sting after touching cold objects, such as shaping snowballs or holding an icy drink. The skin may feel tight, irritated, or painful. Lips and tongue swelling after eating ice cream or consuming cold beverages is another commonly observed symptom. All of these reactions indicate the body’s heightened sensitivity to cold stimuli.
In rare, severe cases, extensive swelling can lead to difficulty breathing or swallowing, especially if the reaction occurs in the throat. Such situations require immediate medical attention.
Treatment and Medical Evaluation
Cold-induced hives usually disappear within a few hours after returning to a warm environment. However, even if symptoms fade quickly, consulting a doctor is strongly recommended. A medical evaluation can determine whether the cold allergy is linked to an underlying condition that requires treatment.
Doctors typically advise reducing exposure to cold as the first line of defense. For individuals living in regions with harsh winter climates, however, avoiding cold air may be nearly impossible. In such cases, physicians often prescribe antihistamines to prevent allergic reactions before they start. These medications are usually taken before going outdoors, especially in cold seasons.
For more severe cases, stronger treatments may be necessary. These can include medications based on monoclonal antibodies, which have been shown to effectively reduce the frequency and intensity of allergic reactions. If the reaction is connected to a chronic illness, addressing the underlying disease becomes the primary step in managing cold allergy.
How to Protect Yourself from Cold Allergy
Prevention is critical. The goal is to minimize direct exposure to cold air, icy surfaces, or cold water, all of which can trigger symptoms. One of the most effective strategies is dressing appropriately. This means wearing hats, scarves, shawls, gloves, and warm outerwear that protect sensitive skin areas from direct contact with cold temperatures. The more insulated the skin is, the less likely it is to react.
Before going outside in cold weather, it is wise to apply a rich, protective cream to exposed skin areas. These creams act as a barrier that helps maintain moisture and reduces the impact of cold air on the skin’s surface. Avoiding cold water — whether for bathing, swimming, or washing hands — is also recommended. Even short exposure can provoke symptoms in people who are highly sensitive.
Finally, staying aware of your body’s reactions will help you adjust your habits. Everyone’s level of sensitivity differs, so learning your personal triggers and avoiding them is essential.
Conclusion
Cold allergy may not be widely discussed, but for those who experience it, the condition can be extremely disruptive and uncomfortable. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and following preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce the impact of cold-induced reactions. Whether through proper clothing, medical advice, or simple lifestyle adjustments, it is entirely possible to live comfortably and confidently — even in cold weather. If symptoms persist or worsen, seeking professional medical guidance is the safest and most effective path toward long-term relief.
Vau.ge – Your Daily Guide for Practical Advice!
Vau.ge is a place where caring for your health, beauty, and daily routines becomes a natural, accessible, and enjoyable experience. Our main goal is to provide you with reliable information about natural remedies, homemade recipes, and practical tips that help you live a healthier life, look better, and simplify your everyday tasks without unnecessary expenses.
Our tips are easy to incorporate into your everyday life — whether it’s skincare, haircare, health-boosting remedies, or small tricks to save time. This knowledge will not only improve your own life but also allow you to share the experience with others, giving more people the chance to live a balanced life naturally and economically.
Please note: The articles on our website are for informational purposes only and do not replace professional medical advice. If you have serious health concerns, please consult a qualified specialist.